D. Bůžek, J. Demel, K. Lang*
Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 14290-14297
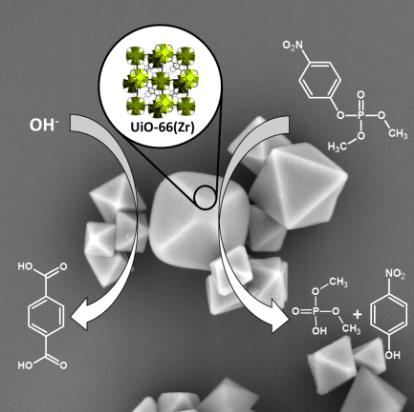
Abstract: Zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks were recently investigated as catalysts for degradation of organophosphate toxic compounds, such as pesticides or chemical warfare agents. The most utilized UiO-66 is considered as a stable material for these applications in aqueous environment. However, the presented results indicate that the properties of UiO-66 are changing considerably in aqueous media under common conditions used for organophosphate degradations, and therefore its catalytic activity is not related to the number of structural defects created during the material synthesis. We delineate the stability of UiO-66 in water of various pHs, the in situ formation of new catalytic sites, and the correlation of these two parameters with the degradation rate of a model organophosphate pollutant, dimethyl-4-nitrophenyl phosphate (methyl-paraoxon). The stability was quantified using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) by measuring the amounts of leached terephthalic acid, the linker of UiO-66, and monocarboxylic acids, the modulators bound at UiO-66 defects. We demonstrate that the HPLC analysis is more suitable method for metal-organic frameworks stability assessment than commonly used methods, e.g., powder X-rays diffraction, adsorption isotherms, or electron microscopy.